2-Minute Neuroscience: Alzheimer's Disease
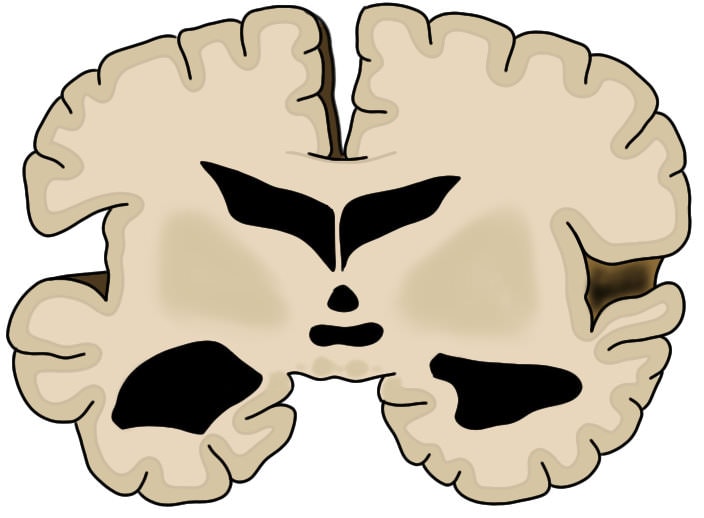
A coronal slice of a brain that has atrophied severely due to the effects of Alzheimer's disease.
In this video, I discuss Alzheimer's disease---the most common form of neurodegenerative disease. In addition to the widespread neurodegeneration that occurs in Alzheimer's disease, there are specific neurobiological abnormalities that appear in the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients. For example, clusters of a misfolded form of a protein called amyloid beta develop around neurons; the clusters are called amyloid plaques. Additionally, clusters of misfolded tau protein develop inside neurons; these clusters are called neurofibrillary tangles. The most common treatments for Alzheimer's disease are acetycholinesterase inhibitors, which are drugs that inhibit the breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is thought to be important to healthy cognition, but acetylcholinesterase inhibitors have relatively modest effects on the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease.